CLASSIFICATION AND ANALYSIS OF TECHNOLOGICAL MACHINES BY THE NATURE OF THE INTERACTION OF THEIR WORKING AND INFORMATION PROCESSES
Abstract
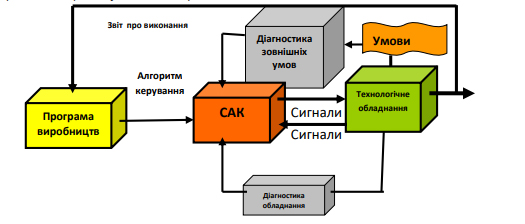
The article describes some problematic issues related to the analysis and classification of technological machines and shows possible ways to improve their perfection in designing based on the use of the latest achievements of intellectual production, development of mechatronics and digital modeling. The purpose of the work is to improve the methods of achieving a given level of quality of technological equipment at the stage of their design, as well as the formation of a new principle for predicting the quality of machines by the controllability parameter.
References
Pavlevich, A.L., Staroverov, N.N., & Heathrich, D.P. (2018). An effective platform for applied research and comprehensive numerical modeling based on ANSYS solutions. CAD / CAM / CAE Observer, 3 (119), 70-75.
Poduraev, Yu.V. (2007). Mechatronics: basics, methods, application. Moscow «Mechanical Engineering».
Rastorguev, G.A., & Rogov, V.A. (2009). Prospects for the Development of Technological Processes in Mechanical Engineering. Technology of Mechanical Engineering, 2, 68-71.
Timchenko, A.A. (2003). Fundamentals of system design and system analysis of complex objects. Kyiv: Lybid.
Ulyanov, V. (2008). Classification of equipment for packaging products in heat-sealed packages. PACKAGE, 2.
Yakhno, O.M., Uzunov, A.V., & Lugovskaya, A.F. (2008). Introduction to Mechatronics. Kiev.
Banaszak, Z., & Pisz, I. (2003). Project–driven production flow management. In. Project Driven Manufacturing. WNT, Warszawa, 53-71.
Gaines, B., & Norrie, D. (1995). Knowledge systematization in the international IMS research program. 1995 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Intelligent Systems for the 21st Century,1, 958-963. doi:10.1109/icsmc.1995.537891 (in English).
Gola, A., & Świć, A. (2013). Design of FFMS Storage Subsystem Using Computer Simulation Method. Actual Problems of Economics, 4(142), 312-318.
Goldman, S.L., Nagel, R.N., & Preiss, K. (1995). Agile competitors and virtual organizations: strategies for enriching the customer. N.Y.: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Groover, M.P., & Zimmers, E.W. (1984). CAD/CAM: computer-aided design and manufacturing. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Camarinha-Matos, L.M., Afsarmanesh, H., & Marik, V. (1998). Intelligent Systems for Manufacturing -Multi-agent systems and virtual organizations. Kluwver Academic Publishers, 130, 137-140.
Krouse, J.K. (1982). What Every Engineer Should Know About Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing: The CAD/CAM Revolution. New York, Basel: Marcel Dekker.
Mauricio Armellini &Tim Pike. (2019). Bank Underground . Bank of England.
Palchevsky, B., Swic, А., & Krestianpol, H. (2015). Computer integrated designing of flexible manufacturing systems. Lublin University of Technology, Lublin.
Palchevskyi, B., Swic, A., & Krestyanpol, H. (2018). Increasing efficiency of flexible manufacturing systems based on computer product grouping. Advances in Science and Technology Research Journal, 12 (2), 6–10 - DOI: 10.12913/22998624/92093
Policymaker’s, A. (30 November, 2016). Guide to Smart Manufacturing.Information Technology & Innovation Foundation (ITIF). Retrieved from
https://www.itif.org/publications/2016/11/30/ policymakers-guide-smart manufacturing.
Prasanth, S. P. Pramod, V.R., & Jagathy Raj, V. P. (2013). Barriers in TPM Implementation in Industries. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research. 2, (5), 28-33. (in English).
Romero, D., Stahre,J., Wuest, T., Noran, O., & Bernus, P. (October, 2016). Åsa FastBerglund and Dominic Gorecky, Towards an Operator 4.0 Typology: A HumanCentric Perspective on the Fourth Industrial Revolution Technologies, International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering (CIE46) Proceedings, Tianjin, China.
Schwaninger, M. (2009). Intelligent Organizations. Powerful Models for Systemic Management. Springer-Verlag, Berlin: Heidelberg.
Tolio, T. (2009). Design of Flexible Production Systems. Methodologies and Tools. Springer-Verlag, Berling: Heidelberg.